Why Sending Sensitive Data by Email Is a Serious Risk
Sending sensitive data by email may seem convenient, but it exposes businesses to serious security risks if not handled properly. But for organizations handling sensitive data, such as legal contracts, financial statements, health records, and proprietary business information, email can also be a significant security risk.
Cybercriminals constantly seek new ways to exploit email vulnerabilities. Whether through human error or poor digital hygiene, a single mistake could expose your organization to data breaches, compliance issues, or financial loss.
The article breaks down five of the most common email mistakes that put sensitive data at risk and offers practical solutions to address them.
1. Sending Unencrypted Emails and Attachments
The risk
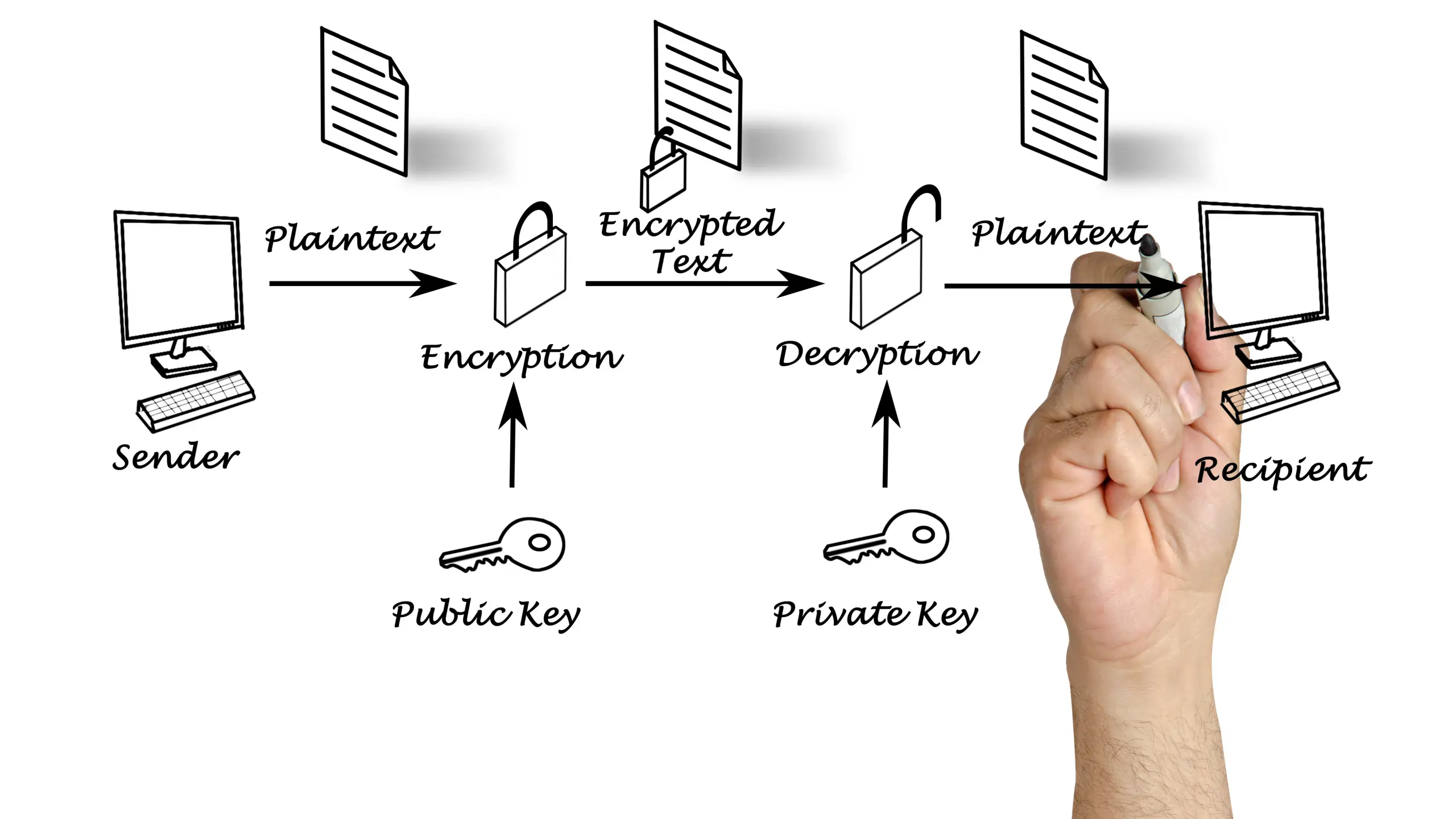
When sensitive data is sent via unencrypted email, it can be intercepted during transmission, especially when it travels over unsecured networks. This includes not just the body of the email but also any attachments, such as contracts or spreadsheets containing confidential information. Most people underestimate how vulnerable email really is, especially when confidential files are sent without proper email encryption.
The solution
Make encryption a standard practice across your organization. Use email services that support end-to-end encryption or enable TLS (Transport Layer Security) by default. For attachments, consider secure file sharing solutions like 689Cloud SecureMail, which encrypts files and enables you to share access-controlled links instead of sending files directly.
Why it matters
Encryption prevents unauthorized access—even if the message is intercepted—by rendering the contents unreadable without the correct decryption key. This adds a critical layer of protection, especially when dealing with financial data, intellectual property, or personal information protected by regulations like HIPAA or GDPR.
2. Oversharing: Sending Emails to More Recipients Than Necessary
The risk:
It is common to CC or BCC multiple people for the sake of transparency. However, when emails contain sensitive information, this approach significantly increases the risk of data leakage. Even trusted team members might forward the email or download files to insecure devices.
The solution:
Implement a “least privilege” policy for information sharing. Emails and file links should only be sent to individuals who absolutely need access to the data. Use platforms like 689Cloud to set expiration dates, watermark documents, and restrict downloads—even after the email has been sent.
Why it matters:
Limiting access reduces your attack surface. The fewer people who have access to sensitive information, the lower the chance it ends up in the wrong hands, whether through negligence or malicious intent.
3. Attaching Files Directly Instead of Using Secure File Links
The risk:
Sending files as direct email attachments is not only outdated but also dangerous. Files can be intercepted, altered, or misused if they fall into the wrong hands. You also lose control of the document once it’s downloaded.
The solution:
Use a secure cloud-based file sharing platform like 689Cloud, which encrypts files in transit and at rest. Instead of attaching files, share an encrypted link with controlled access permissions. You can track who opens the file, restrict downloads, revoke access anytime, and even apply digital watermarks.
Why it matters:
Secure file links give you visibility and control. You will know who accessed the file, when, and from where, providing critical insights for auditing and compliance purposes.
4. Using Weak or Reused Passwords
The risk:
Many employees still use weak passwords like “123456” or reuse the same password across multiple platforms. If just one of those platforms gets compromised, it could provide attackers with access to corporate email accounts.
The solution:
Require strong, unique passwords for all business email accounts. A strong password includes a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and is at least 12 characters long. Encourage the use of password managers to store and generate complex passwords securely.Additionally, multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be implemented across all email accounts and file-sharing platforms to provide an extra layer of security.
Why it matters:
Strong credentials and MFA can stop unauthorized access even if a password is stolen or guessed. According to Microsoft, MFA can prevent 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
5. Ignoring Cybersecurity Hygiene: No Antivirus or Anti-Malware Protection
The risk
Opening email attachments without proper security software exposes your organization to ransomware, spyware, and other malicious threats. Attackers often use email as the initial vector to gain a foothold in your network.
The solution
Install enterprise-grade antivirus and anti-malware software on all company devices. Keep the software updated and set up automatic scans. Train your team to recognize phishing emails, suspicious attachments, and other red flags.
Why it matters
Cyberattacks are often preventable with the right tools and awareness. Preventive security tools reduce the chance that a malicious file or email will compromise your systems or data.
Best Practices for Sending Sensitive Data via Email
To reinforce secure file sharing and communication across your enterprise, follow these best practices:
- Use encrypted email services like ProtonMail, Gmail (with TLS), or Outlook with built-in security features.
- Avoid attachments—share encrypted file links using cloud-based platforms such as 689Cloud.
- Enable access controls: Set permissions like view-only access, download restrictions, and expiration dates.
- Apply multi-factor authentication to all email and file-sharing accounts.
- Train employees regularly on email security, phishing awareness, and data handling policies.
- Keep software updated to patch known vulnerabilities in operating systems, browsers, and email clients.
Final Thoughts: Secure Communication Is a Business Imperative
Safeguarding sensitive data isn’t just an IT concern, it is a business-critical priority. Email remains a high-risk vector for data breaches, but with the right policies, tools, and training, these risks can be effectively mitigated.By adopting secure file sharing platforms like 689Cloud, enforcing encryption standards, and promoting cybersecurity hygiene across your organization, you’ll dramatically reduce the risk of data leaks and protect your company’s reputation, compliance, and bottom line.Protect what matters. Choose secure, encrypted file sharing with 689Cloud SecureMail to keep your communications safe, compliant, and under your control.
FAQ
1. What’s the safest way to send sensitive data by email?
The safest method is to avoid sending unprotected attachments. Instead, organizations should use encrypted file-sharing tools or rights-managed email solutions such as those that apply access control, watermarking, and download restrictions.
2. How can I make sure recipients can’t forward or copy my email attachments?
Traditional email clients cannot prevent forwarding or copying once a file is opened. However, solutions using Information Rights Management (IRM)—including services like 689Cloud SecureMail—allow senders to disable forwarding, copying, screenshotting, or printing depending on policy settings.
3. Does encryption alone protect sensitive documents?
Not completely. Encryption protects files during transmission, but once decrypted on the recipient’s device, most email attachments become unprotected. IRM-based tools add an extra layer of security by keeping files encrypted and access-controlled even after download.
4. How can businesses track who opens or downloads a sensitive file?
This requires audit logging, which standard email does not provide. IRM platforms like 689Cloud generate audit trails showing when a file is opened, viewed, downloaded, or attempted to be shared, giving organizations full visibility into document usage.